| www.Travel-To-Halkidiki.com - HALKIDIKI ISLAND GUIDE | |
 |
||
|
|
|
| -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
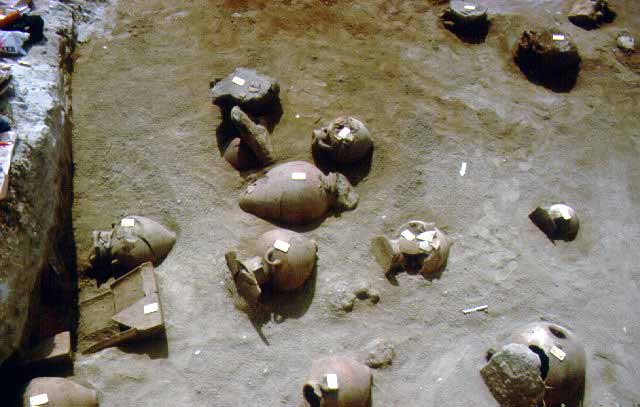
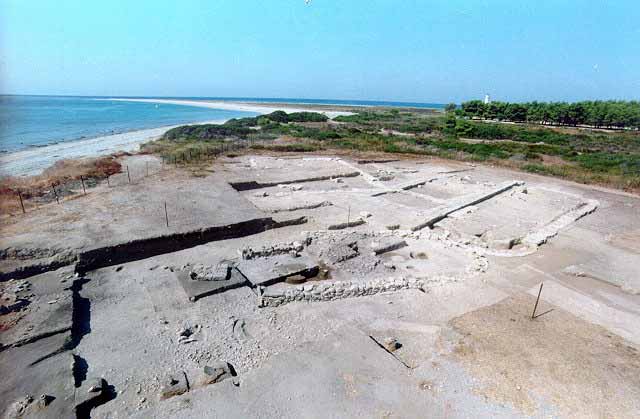
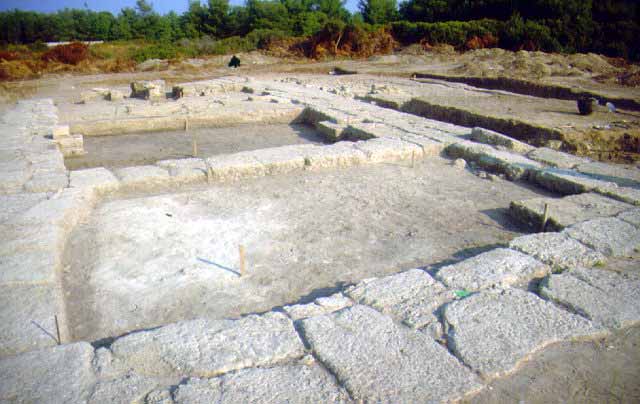
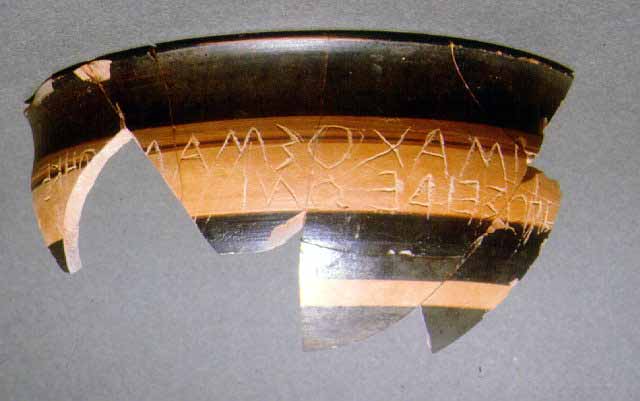
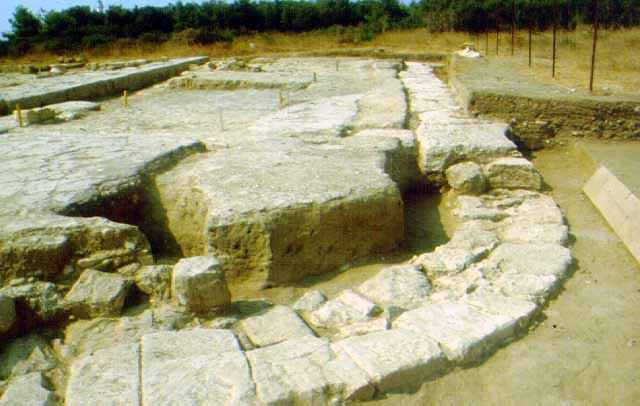
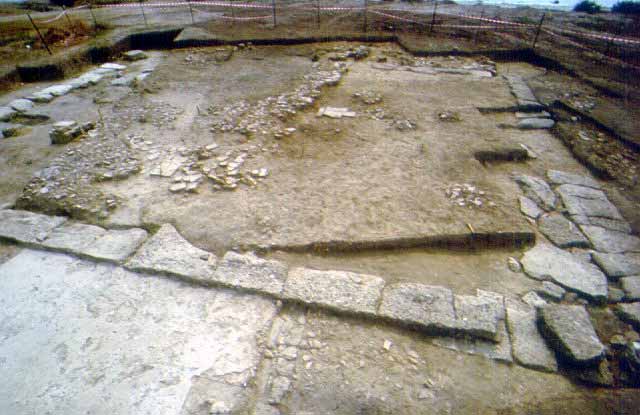
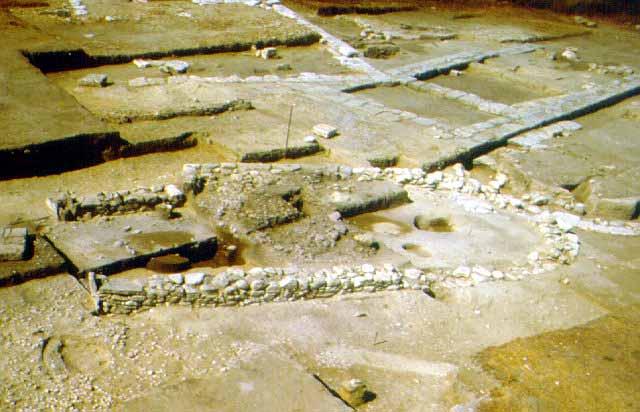
WORTH SEEING PETRALONA CAVE MOUNT ATHOS ARCHAEOLOGICAL MUSEU AKANTHOS MENDI NEA RODA SANCTUARY OLYNTHOS MACEDONIAN TOMB OF P ANCIENT STAGEIRA THE TOUBA AT AGIOS M HALKIDIKI HOTELS RESTAURANT RENT A CAR TRAVEL AGENCY MAP INFORMATION VILLAGES BEACHES WORTH SEEING PHOTO GALLERY VIDEO GALLERY 360 PANORAMAS E-CARDS TOPICS MAILING LIST NEWS SEARCH ABOUT US LINKS |
|

 ABOUT
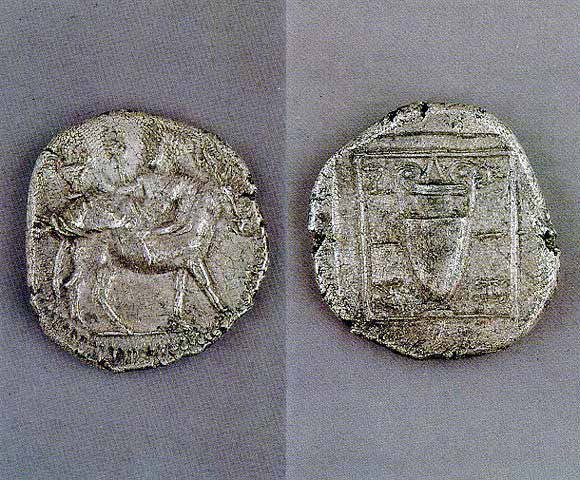
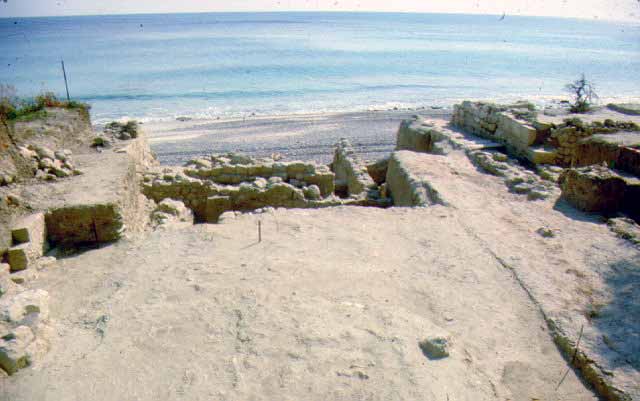
MENDI
ABOUT
MENDI















